In marketing or sales, we typically start talking about growth using funnels. A funnel usually starts with marketing at the top level, which drives product development and sales. Though useful, this framework falls short once marketing brings in low quality leads which trickles down to the bottom of the funnel (Gajdhar, 2020).
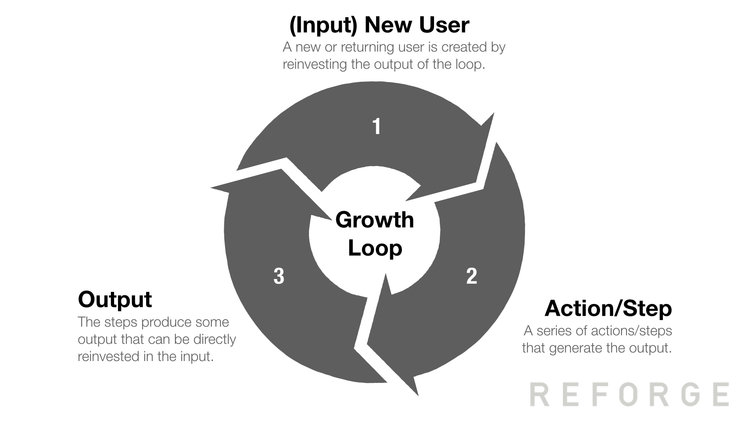
The shortcoming of the funnel framework can be remedied by using the concept of growth loops. Some of the fastest growing products nowadays are best represented as a system of loops, not funnels. Being closed systems, loops generate more output that can be reinvested in the input through various processes. Different growth loops serve different purposes for value creation which may include: new users, returning users, defensibility, or efficiency (Balfour et.al, n.d.)
Benefits of Growth Loops
Loops fundamentally help you determine how to use and reinvest the output of a cycle of the loop into another, resulting in more output that can be reinvested again and vice versa. Loops, create a compounding effect for the product, instead of just a linear effect. This is essential to sustainable growth.
The following three core elements should be found in each step of the loop:
- What – the action or activity happening in the loop
- Who – the entity (company, user, supplier, etc.) doing the action
- Why – the reasons or incentives in taking that action
An example of a company that utilized a growth loop is Pinterest:
Behind Pinterest’s growth is the following loop:
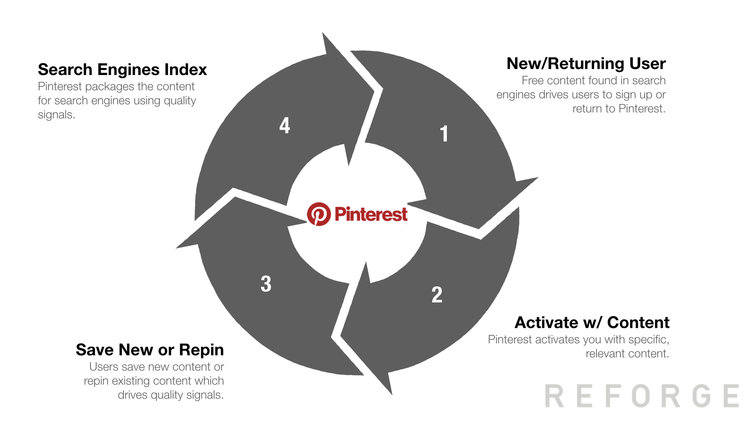
- User signs up or returns to the site
- Users are activated on the product with specific/relevant content
- Users save new content or repin existing content. This gets Pinterest quality signals
- Pinterest distributes the quality content to search engines
- User finds the content via search engines and either signs up/returns
Users come back to the platform to revisit the cool images that they saved and also gain praise from friends or other users when their pins are seen around the platform. This is the third step which is Pinterest’s loop, the incentive for users to repin or save new content comes from the need to gain personal and/or social capital.
A growth model starts with understanding evaluating the user persona, intent, and behavior. Once you have identified these, you can add metrics to each stage and start with baseline data to form a growth mode.
References:
Balfour et. al (n.d). Growth Loops are the New Funnels. Retrieved on June 8, 2021 from https://www.reforge.com/blog/growth-loops
Gajdhar, S. (2020). Growth Loops: A Paradigm Shift in Growth Strategies. Retrieved on June 8, 2021 from https://clevertap.com/blog/growth-loops/#:y=:text=Growth%

